"A bitter lesson", the scientist said that 70 years in the field of research in AI has been spent practically in vain
 Source:
Source:
The biggest lesson that can be drawn from 70 years of research in AI, is that the common methods using calculations ultimately prove to be the most effective — and by a wide margin. The ultimate cause of this is Moore's law. Or rather, his generalization of continuous, exponential reduction of computational processors. This "bitter lesson," said Richard Sutton, canadian computer scientist. Hereinafter in the first person.
the
Why artificial intelligence researchers were stumped for 70 years?
Most of the artificial intelligence research was conducted as if the calculation agent were constant (and in this case, the use of human knowledge would be one of the only ways to improve performance). But after some — more than necessary for a typical research project will inevitably become far more available computing. In search of improvements that can help in the short term, scientists are trying to use the maximum of human knowledge in this area, but the only thing that matters in the long run is the growing use of computing. These two aspects should not contradict each other, but in practice go. The time spent on one of them, does not equal time spent on the other. There is a psychological obligation to invest in a particular approach. But an approach based on human knowledge, has a tendency to complicate methods so that they become less suited to take advantage of the common methods using calculations.
Conclusion: should immediately reject the attempt to solve the problem of AI's "head" because it will take time and it will be solved much faster and easier — thanks to the growth of computing capacity.
There Were many examples where researchers in AI belatedly realized this bitter lesson. It will be instructive to consider some of the most outstanding examples.
In computer chess methods that defeated world champion Kasparov in 1997, was based on massive, thorough search. At that time, to them with anxiety treated most researchers of computer chess, which used methods based on the understanding of the special structure of chess. When more simple, based on the search approach with special hardware and software was much more effective, the researchers pushed off from the human understanding of chess, did not admit defeat. They said, "this time the approach of brute force, can be defeated, but that he will not become a common strategy, and certainly people don't play chess that way. These scientists wanted methods based on human contribution, won, and very disappointed when this did not happen.
Conclusion: simple brute force computing will take its toll sooner or later.
A Similar pattern of progress in research were seen in the computer, only with a delay for another 20 years. Initially, great efforts were directed to avoid using human knowledge or features of the game, but all these efforts proved useless, or even worse, as soon as search used effectively and on a large scale. It was also important to use the learning during independent play to learn the value function (as in many other games and even in chess, the only training did not play a big role in the program of 1997, which first defeated the champion of the world). Learning to play with yourself, learning in General, it's like a search that allows you to apply massive amounts of computing. Recruiting and training are two of the most important class of techniques that involve huge amounts of calculations in the research of AI. In computer go, as in computer chess, the initial research efforts were focused on the use of human understanding (to use less), and only much later was achieved much greater success through the use of search and learning.
Conclusion: search and training, energized processing power far superior to attempts to solve the problem of "unconventional way of thinking."
In the field of speech recognition in the 1970-ies was carried out a contest sponsored by DARPA. The participants represented various methods that used the benefits of human knowledge — knowledge of words or phonemes, the human vocal tract and so on. On the other side of the fence was newer methods, statistical in nature and performs more calculations, based on hidden Markov models (HMM). And again, statistical methods win methods based on human knowledge. This has led to major changes in the whole natural language processing, gradually emerging for decades, yet in the end, statistics and computing began to dominate the field. The recent rise of deep learning in speech recognition is the last step in this consistent direction. Methods deep learning is even less rely on human knowledge and use more computing, along with training on a huge set of samples, and give a stunning speech recognition system.
Richard Sutton, canadian computer scientist
As in games, scientists have always tried to create a system that will work the way they imagined in their heads — they tried to put this knowledge in their systems but it all came out very unproductive, scientists just wasting time until — because of Moore's law — became increasingly available massive compute and find of itself fine application.
Conclusion: the same error was repeated for decades
A Similar picture was and in the field of computer vision. The first methods was seen as a search of some of the contours of generalized cylinders, or by using SIFT (scale-invariant transformation characteristics). But it's all thrown into the furnace. Modern neural networks deep learning only use the concept of convolution and to certain invariants and work much better.
This is a big lesson.
In whatever area we look, we all continue to make the same mistakes. To see this and to fight effectively, you need to understand why these errors are so attractive, We must learn the bitter lesson that the construction of how we think, starting from how we think doesn't work in the long term. A bitter lesson, based on historical observations, shows that: 1) researchers in AI often tried to embed the knowledge into their agents; 2) it's always helped in the short term and brought it to scientists satisfaction; 3) but in the long run, everything came to a standstill and hindered further progress; 4) progress is inevitable breakthrough came with the use of an opposite approach, based on scale computing by a search and learning. The success was bitter taste and is often not absorbed completely, because the success of the computation, and not the success of human-oriented approaches.
From this bitter lesson you should learn one thing: the immense power methods General purpose methods, which continue to scale with the growth of the operation even when the available computing becomes very large. Two methods that seem to arbitrarily massturbate so is the search and training.
The Second thing to be learned from this bitter lesson is that the actual content of the mind is extremely and unnecessarily complex; we should stop trying to find simple ways to reflect on the content of the mind, like the simple ways of thinking about space, objects, multiple agents or symmetries. They are all part of arbitrarily complex external world. We should not try to push because of their infinite complexity; we should build on the meta-methods that can find and catch this in arbitrary complexity. These methods can find good approximations, but the search for them should be our way, not us. We need agents AI that can open as well as we, and not contain what we discovered. Building on our discoveries only complicates the process of discovery and searching.
Conclusion: you have to trust the calculation rather than try to trace the human thinking and attempts to explain the complex methods of discovery and the search for simple schemes; long-term work first, not last.
Discuss the bitter lesson of researchers in AI can be .
Recommended
Can genes create the perfect diet for you?
Diet on genotype can be a way out for many, but it still has a lot of questions Don't know what to do to lose weight? DNA tests promise to help you with this. They will be able to develop the most individual diet, because for this they will use the m...
How many extraterrestrial civilizations can exist nearby?
If aliens exist, why don't we "hear" them? In the 12th episode of Cosmos, which aired on December 14, 1980, co-author and host Carl Sagan introduced viewers to the same equation of astronomer Frank Drake. Using it, he calculated the potential number ...
Why does the most poisonous plant in the world cause severe pain?
The pain caused to humans by the Gimpi-gympie plant can drive him crazy Many people consider Australia a very dangerous place full of poisonous creatures. And this is a perfectly correct idea, because this continent literally wants to kill everyone w...
Related News
Google was unable to confirm the existence of cold fusion
Spending years on research and experiments and invested a considerable amount of money in this enterprise the company has not any proof that nuclear fusion can be carried out at room temperature. However, investments in the amount...
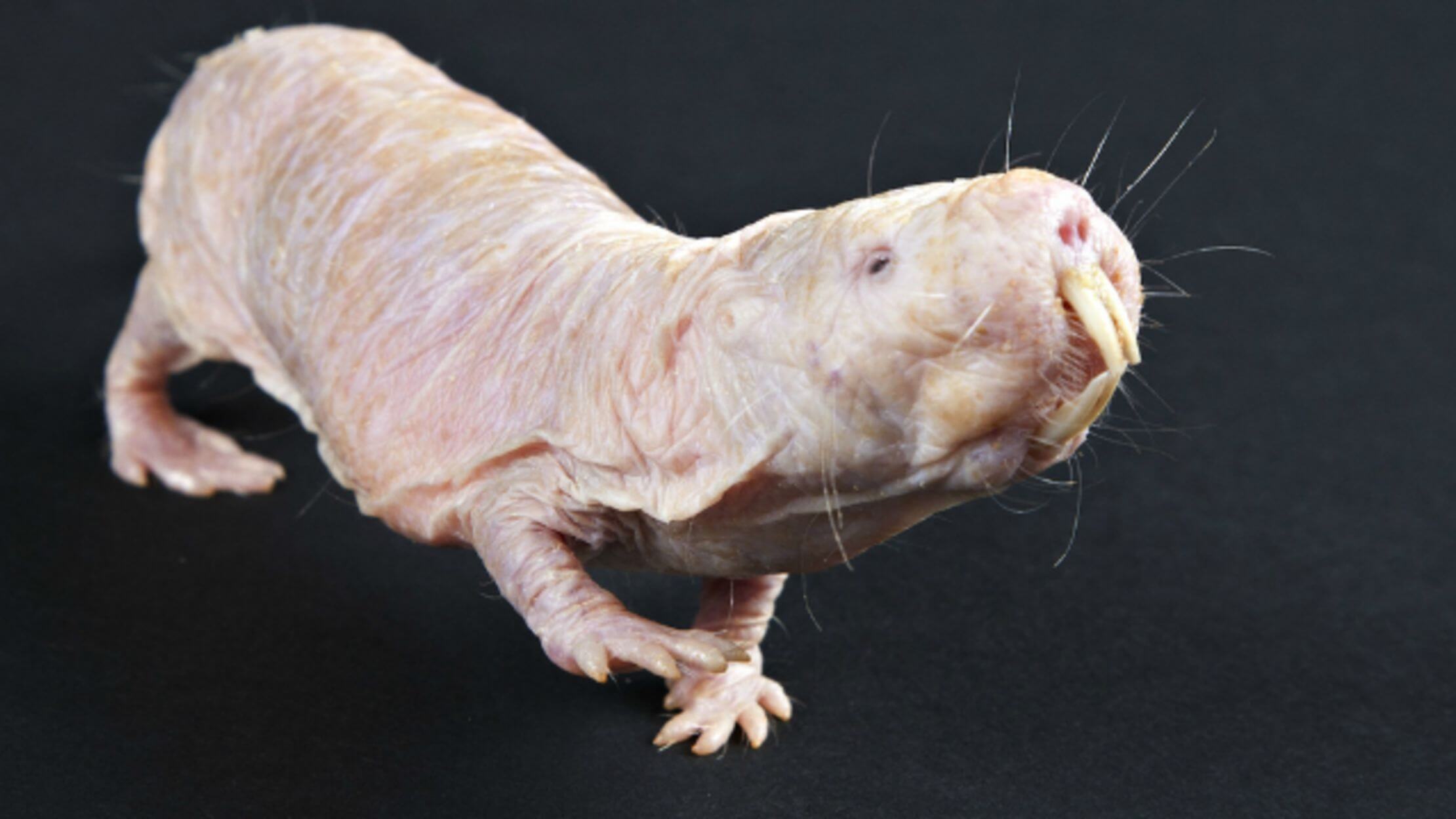
Rodents-superheroes: naked mole rats don't feel many kinds of pain
New research shows that several species of African naked mole develops a supernatural ability to endure certain types of pain, including discomfort caused by acid, chili pepper, and hot mustard. This news may ultimately lead to an...
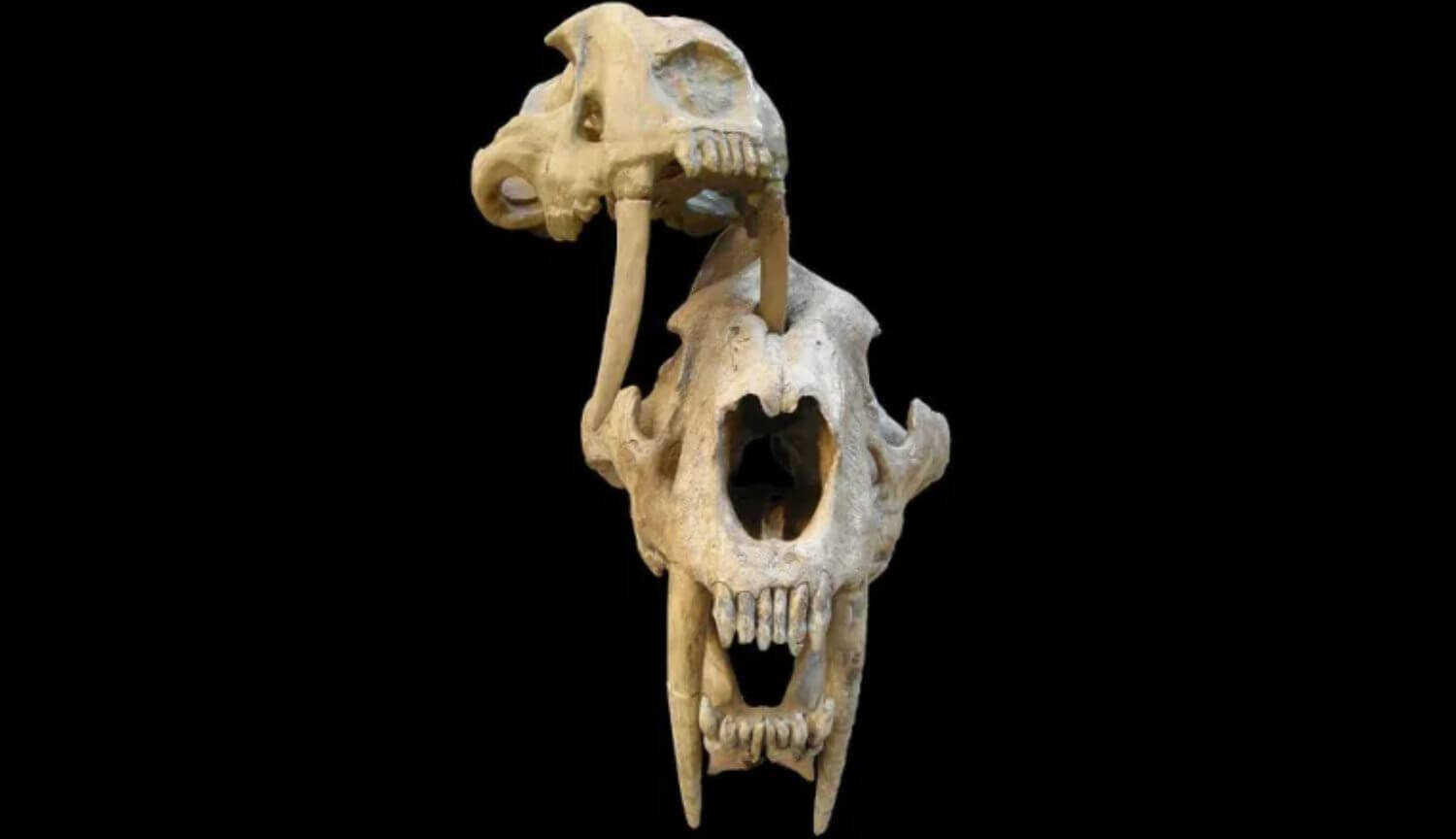
Saber-toothed tigers were stronger than previously thought
the purpose of the huge fangs of saber-toothed tigers a long time is the cause of disputes between different scientists. Some researchers believe that the ancient cat killed his victims only with sharp claws and fangs were only us...
Warner Music has signed the first ever contract with artificial intelligence
the impression that people are not just resigned to the fact that artificial intelligence creates works of art for which they are willing to pay a tidy sum — more than that, people welcome it. And in response to the artificial int...
Although neuroscientists have made amazing progress, the origin of consciousness in humans and its nature and processes still remain largely unknown; the basic physiological mechanisms that make creatures conscious, is still not e...
"Not detectable" in NASA admitted that we are blind to the signs of alien technology
In recent months several leading astrophysicists from NASA and Harvard have suggested that aliens are a figment of science fiction: the developed and the ancient technological civilization may exist but are beyond our comprehensio...
Born first in the history of macaques-rhesus sperm from frozen testicles
a Procedure that involves the removal and freezing of immature testicular tissue with the subsequent implantation, led to the first live birth of a healthy monkey. This technique can theoretically help the boys goubernator period,...
Impossible scenario: the scientists observed the movement of heat on the speed of sound
Ryan Duncan froze. Only that he had a new experiment to study ordinary graphite is the same, their pencil — but the results seemed impossible physically: the heat that normally dissipates slowly passed through the graphite at the ...
Officially confirmed the extinction of the first species of mammal due to global warming
Australian authorities have officially recognized the extinction of the first species of mammal due to global climate change. We are talking about reef mosaicisti rat (Melomys rubicola). A message in a new report, which the govern...
NASA wants to explore another asteroid using a new automatic probe
the space Agency NASA is considering launching robotic probes to study another large asteroid in the Solar system – Pallada. According to the portal Space.com the decision to send the apparatus to the object whose orbit is about 2...
Scientists have found differences between serial killers, male and female
the vast majority of serial killers are men, but there are also plenty of evidence that they can be women. Generally, the first serial killer in history can be considered a woman by the name , which made a lot of poisoning in Anci...
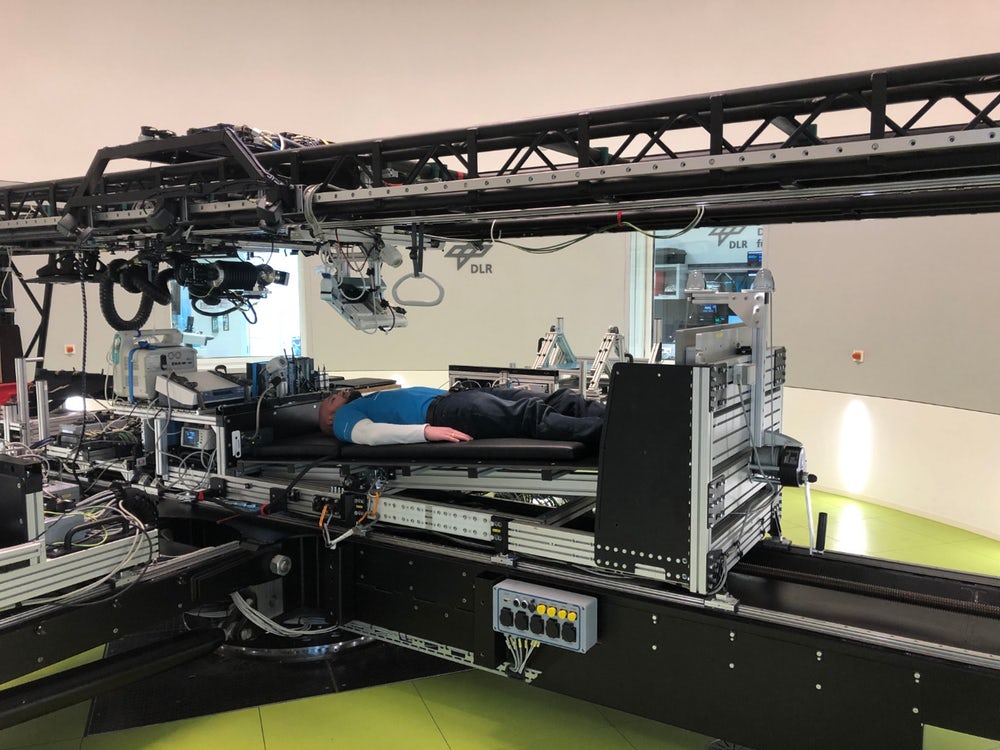
In the new experiment, NASA astronauts will have two months to lie still on the bed
Space travel in zero gravity have on the human body destructive influence. Due to earth gravity people Willy-nilly to keep their body and their muscles are constantly trained. In zero gravity, the muscles all relaxed and quickly a...
Why with age, time flies faster than in childhood?
In the course of growing up-almost every person there is a feeling that over time greatly accelerated, it would seem that he only recently woke up and it was time to go to bed. For many years scientists tried to identify the cause...
Tuberculosis can be defeated until 2045
can eradicate TB until 2045, if the fight against the deadly disease will be properly funded, said the group of international experts. According to them, the inaction will result in huge economic and social costs, and the world n...
Superconducting nanowires are planning to use to search for dark matter
One of the greatest scientific research of our time is the hunt for dark matter. Physicists believe that this substance fills the universe and think you can see evidence of this in how to spin the galaxy. The fact that galaxies ro...
Boris Katz has built a career helping the machines to learn the language. He believes that the current AI technologies are insufficient to make Siri or Alexa really smart. Siri, Alexa, Home technologies, which analyze the language...
How poor sleep leads to heart disease and death?
According to the world health organization, the reason for 31% of all deaths in the world are cardiovascular diseases. They develop in the wrong diet, Smoking, lack of exercise and irregular sleep mode. If scientists already know ...
The asteroid Bennu was more active than thought
the study of the surface of the asteroid Bennu with the help of the spacecraft OSIRIS-REx revealed some interesting features of this small celestial body. It turns out that the object covered a much larger number of craters than e...
Proven that some people can feel the changes in the magnetic field
Many animals, including some species of birds, sea turtles and some species of bacteria have a special "navigation system" that allows them to feel and use the Earth's magnetic field as a compass. This ability is called magnetorec...
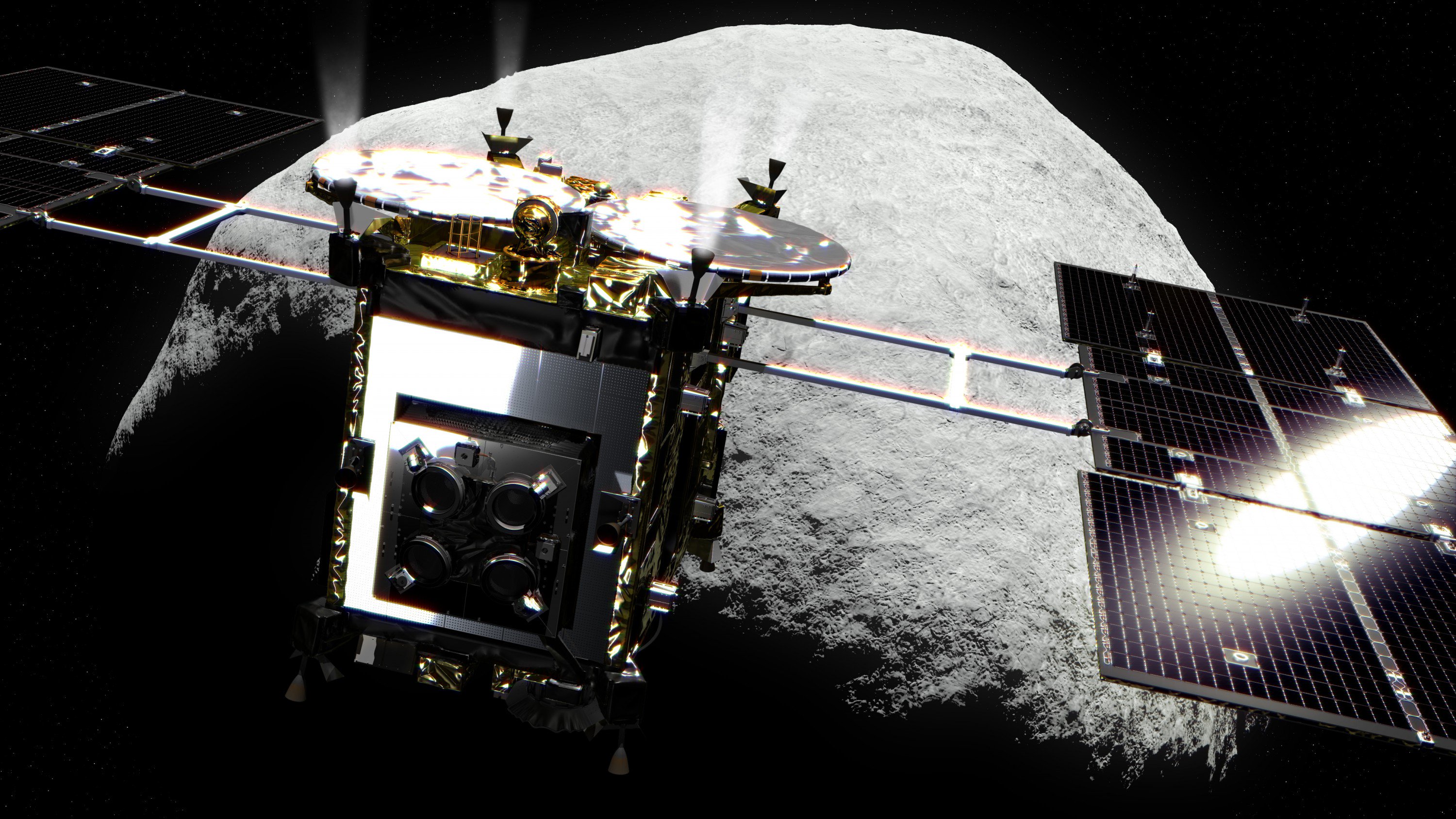
Japanese probe "Hayabusa-2" will play the bombing of the asteroid Ryugu 5 APR
the Japanese aerospace exploration Agency (JAXA) announced future plans regarding the mission of the spacecraft "Hayabusa-2", which last month landed on the asteroid Ryugu and its ground, after being shot in the surface of the obj...

































Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!