How to change the life, if the energy will be free?
 Source:
Source:
The Development of technology leads to the fact that the value of many things tends to zero. What we once paid so much, now is cheap or even get for free is to buy a computer, to call on the other end of the world, take a photo, watch a movie, listen to music or even go to another country. More and more things will join this list. Perhaps one day there will be electricity. Pretty cool, huh? After all, free. Who doesn't love free?
The energy Issue is very complex, really.
The Cost of burning coal is already not falling, but the cost of collecting solar energy continues to fall. In October 2017 the electricity bill in Saudi Arabia fell to 1.79 cents (this is on average five times cheaper than in Russia) per kilowatt-hour, beating the previous record in Abu Dhabi (2.42 cents kWh). Not surprisingly, these incredibly low prices are a legacy of the sunniest parts of the world. In other parts of the world, both in the US and in Russia, prices fluctuate at the level of 5-13 cents per kWh
Whenever we think prices can't fall off, they fall — and the best thing about this constant price decline is that this happens not because of the batteries. Cheap and efficient batteries still lag far behind the overall pace of development of energy systems and especially renewable sources of energy. But as soon as we learn how to properly and cheaply save the energy constraints will be very little. And also the reality will become transparent solar cells that will turn each outer surface of the glass into a small plant.
What will the world with free electricity? Electricity would be ubiquitous in many parts of the world, where else did not. Other places will disappear electricity bills. Production costs will fall, will drop transport costs and all associated costs.
The Money we save on energy could be spent on social programs or even to create a universal basic income, which will help to build a just society. If everything is cheaper, we will not have to work more to earn more money, which means we will free up your time and we will be able to direct it in a creative direction.
And yet, every coin has a flip side, and the old adage that the best things in life come for free in this case does not work. Let's see what happened when we did other free or cheap resources.
In the United States has made food cheap and abundant by learning how to produce it in scale — and the problem became worse than ever. We produce plastic bottles and packages for a penny, and now the oceans are crammed with cheap and non-degradable waste.
The Jevons Paradox is that as soon as technological progress increases the efficiency of the product or resource, the rate of consumption of that resource grow due to growing demand, which directly reduces the efficiency of the savings. In the end, deep down in his nature of humanity only takes, and electricity is no exception.
The middle East countries where the price of electricity is the lowest in the world, became a shining example. Excessive energy use has become commonplace, and there is no incentive to rein him in. Ideally, the energy consumption per capita should be reflected in GDP per capita, but countries such as Kuwait, Bahrain and Saudi Arabia, have an imbalance in this metric, using more energy than necessary to achieve its GDP.
As in other parts of the world energy will be cheaper, people will use it more and more, and the first victim will be the planet. Despite the fact that the energy is renewable, it does not mean that the environment will remain in order; can be consequences that we cannot even imagine yourself as the one who invented plastic, never imagined that poison marine life.
Since energy is becoming cheaper and eventually moves to zero value, we have to use ingenuity to use it wisely. Government regulation can play a role, as well as market forces, despite the absence of economic incentives. As with any new technological development, we can have phase adjustments when we go too far, catch yourself by the tail and peel back ago.
The free, clean energy will undoubtedly bring many benefits. But we can't afford to forget that for free, someone pays — and it's not always immediately obvious.
Recommended
Mystery of the Sargasso sea, and why there were dead ships
At the time, in the Sargasso sea lost a lot of ships. Almost all mystical place, about which people say, giving them a mysterious halo, are on the water. When ”ends”, the disappearances do seem very strange and inexplicable. One of the places that ar...
An air leak site has been found on the ISS. What's next?
Air leak occurs in Russian station module Inside the International Space Station live astronauts from different countries and all of them need oxygen. The air needed for the life of the crew is produced by special equipment, but the tightness of the ...
Why can thinking about death make life happier?
Awareness of one's own mortality can be a liberating and awakening experience How do you feel about the idea of death? How often do you think about it and what emotions do you feel? Many of us have been pondering these questions lately. The pandemic ...
Related News
How does it work? | How does the shipping lock
the First shipping lock, which was carried out alternating the alignment of the water level, was invented by Qiao, Value 984 year and built on the Great Chinese channel. The gateway was a straight section with a length of 76 meter...
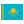
Fly Elephant: first flying 3D printer
it would Seem than can surprise manufacturers of 3D printers, even if liquid metal can be used for printing? But the Chinese company DediBot all the same managed to do something unique: flying a 3D printer Fly Elephant. Well, if y...
How does it work? | Rail cable car
last week we told you about how to operate a gondola, but today we will focus on a different type of cable cars — rail. Vehicles that carry passengers on them or the goods are called funiculars. First use of the funicular as...
How does it work? | Cable-cableway
In 1834, the German engineer albert Vogts invented the metal rope of intertwined steel wires. And after three decades in the North of Switzerland near Schaffhausen has introduced the world's first cable car for passengers. With it...
the First escalator in the form of "circle stairs" was patented by the American inventor Nathan Ames in 1859, however, it has never been used. Almost 30 years later, in 1892, the American Jesse Reno patented the "inclined lift". I...
How does it work? | Introscope
introscope — it is a special x-ray device allowing for the study of internal structure of object and processes without having to open. The endoscopes are widely used for inspection of personal belongings at airports, railway...
The company Facebook has introduced a new unit of time
We are accustomed to the fact that time is measured in seconds, minutes, hours, months, years and so on. In the case where high accuracy is required, we use milliseconds or nanoseconds. It would seem, why invent the wheel and intr...
How does it work? | BitTorrent
BitTorrent — is a network Protocol for exchanging files over the Internet. It was created by American computer programmer Bram Cohen, who wrote the first torrent client "BitTorrent" in Python in April 2001. Files according t...
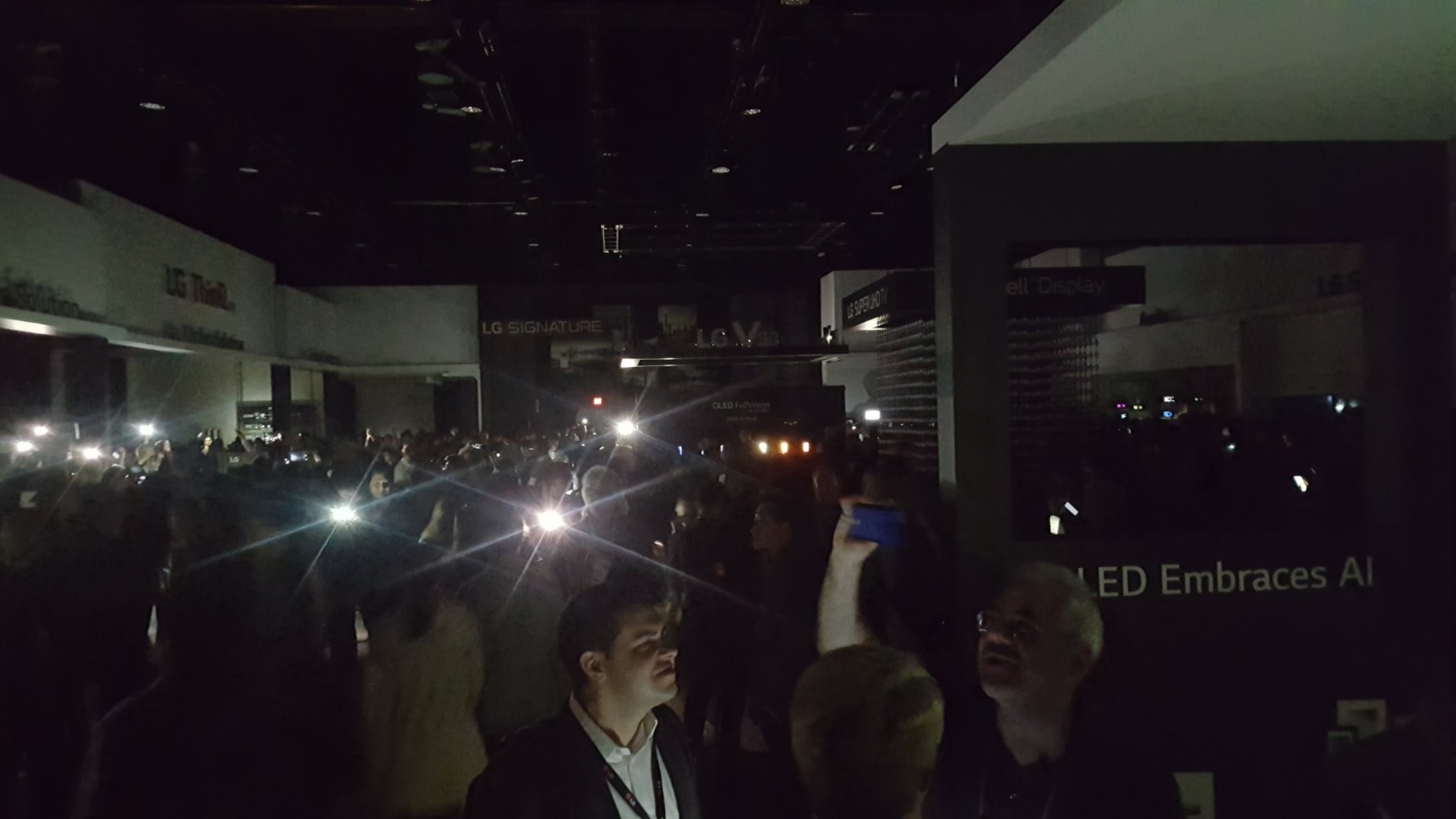
#CES 2018 | the Visitors had to spend several hours in the dark
a Few hours ago one of the largest technology exhibitions in the moment, the Las Vegas Convention Center, are actually frozen. The fact that the premise of almost 58 thousand square meters of unexpectedly plunged into darkness at ...
the Wi-Fi was created in 1998 in the laboratory of radio astronomy in CSIRO in Australia. The Creator of the wireless communication Protocol is engineer John O'sullivan. The term "Wi-Fi" was originally coined as a play on words wi...
Bluetooth — it is a technology for wireless transmission of data between devices at a distance up to 100 meters. Work on the creation of Bluetooth was started in 1994 by a manufacturer of telecommunication equipment Ericsson...
How does it work? | Sleep tracker
it is known that human sleep consists of repetitive cycles of REM and NREM sleep. The average duration of each cycle is approximately one and a half hours. A good rest is sleep, which includes 5 full cycles. Thus, for maximum effi...
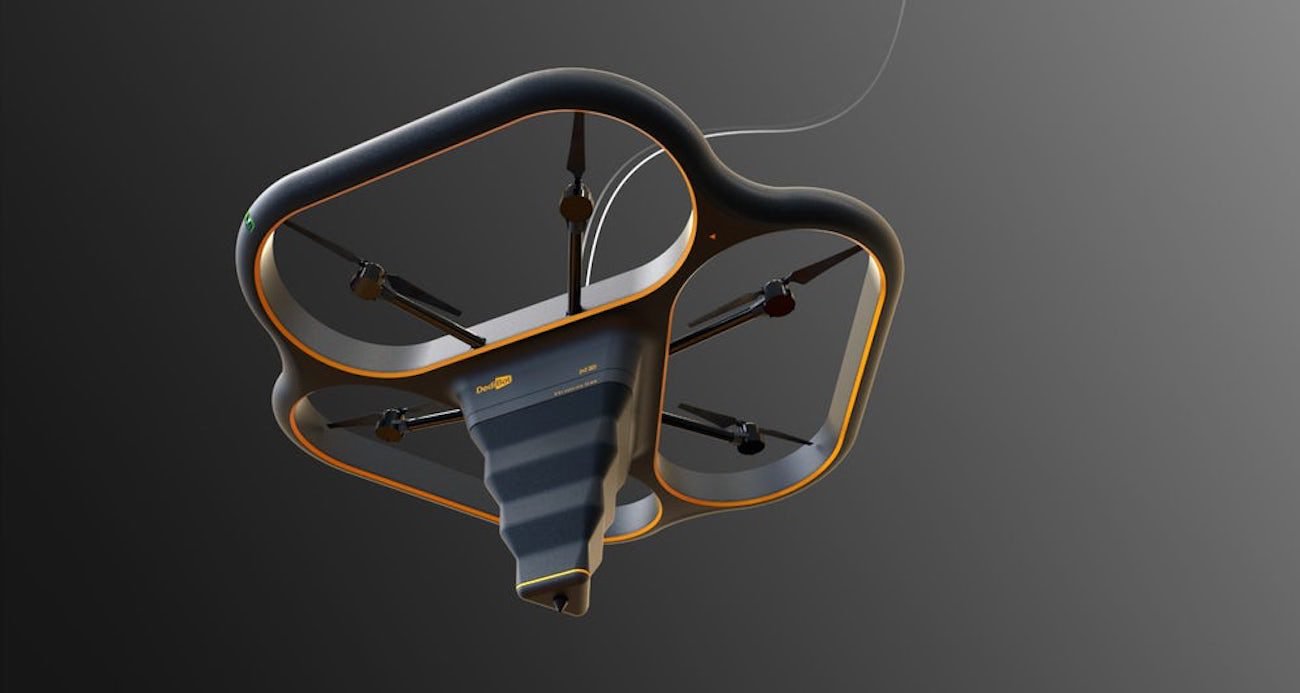
the First pedometer was invented by the French mathematician Jean Fernely in 1525. The device was a system of gear wheels and gears that are driven by an oscillating lever. He spun the arrows on the four dials, which are consisten...
How does it work? | Portable heart rate monitor
Monitor — a device for monitoring heart rate in real time. Electrical activity of the heart was opened in the late 19th century, and in 1902, Willem einthoven was the first, who is technically registered with a string galvan...
How does it work? | A quantum computer
a Quantum computer is a computing device that uses the phenomena of quantum mechanics to transmit and process the data. The idea of quantum computing was independently proposed by Yuri mininum and Richard Feynman in the early 80-i...
How does it work? | Satellite navigation system
the Idea of creating a satellite navigation system was born in the 50-ies of the last century. American scientists led by Richard Kershner watched the signal coming from the Soviet satellite, and found that due to the Doppler effe...
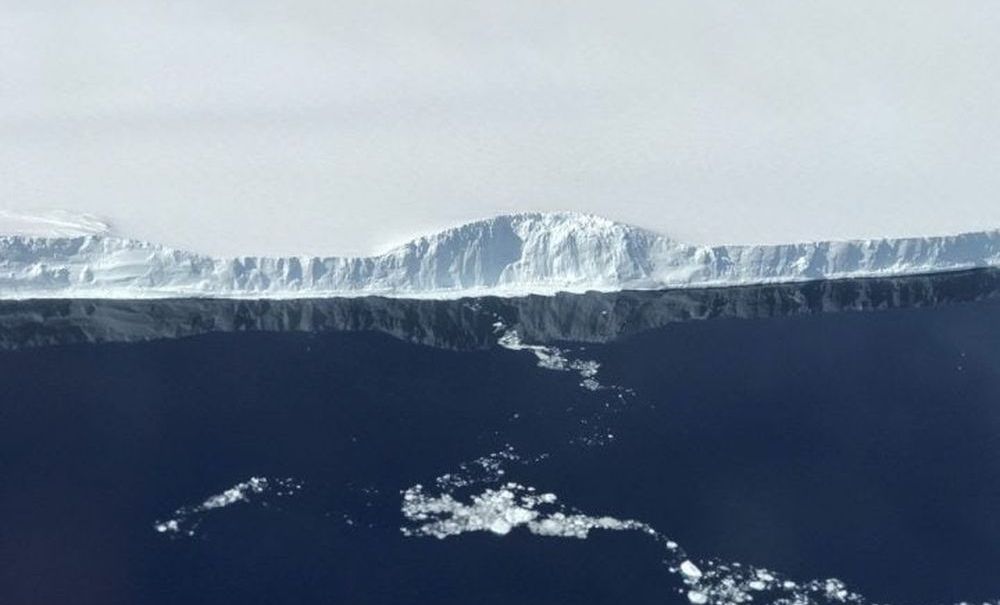
#photo of the day | NASA published pictures of a giant iceberg separated from Antarctica
in July this year, one of the largest in the history of our planet iceberg A-68A is separated from of the Larsen ice sheet in Antarctica. It is difficult even to imagine a giant piece of ice with an area of over 6000 square kilome...
How does it work? | Rain sensor
the Car rain sensor is an optic-electronic device, which is installed on car windshield and responds to hydration. It is necessary for the determination of moisture and automatically turn on the wipers. The first experiments to cr...
How does it work? | Fire sensor
the First automatic fire sensor was heat. It was created by Americans Francis Upton and Fernando Dibble in the late 19th century. The design of the sensor was an electric battery, bell dome, a magnet in an open circuit and a therm...
How does it work? | Motion sensor
the motion Sensors are widely used in security systems to detect intrusion, as well as for automation of lighting and HVAC equipment in homes and offices. Analysts expect growth in the use of motion sensors by 14% annually until 2...






































Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!